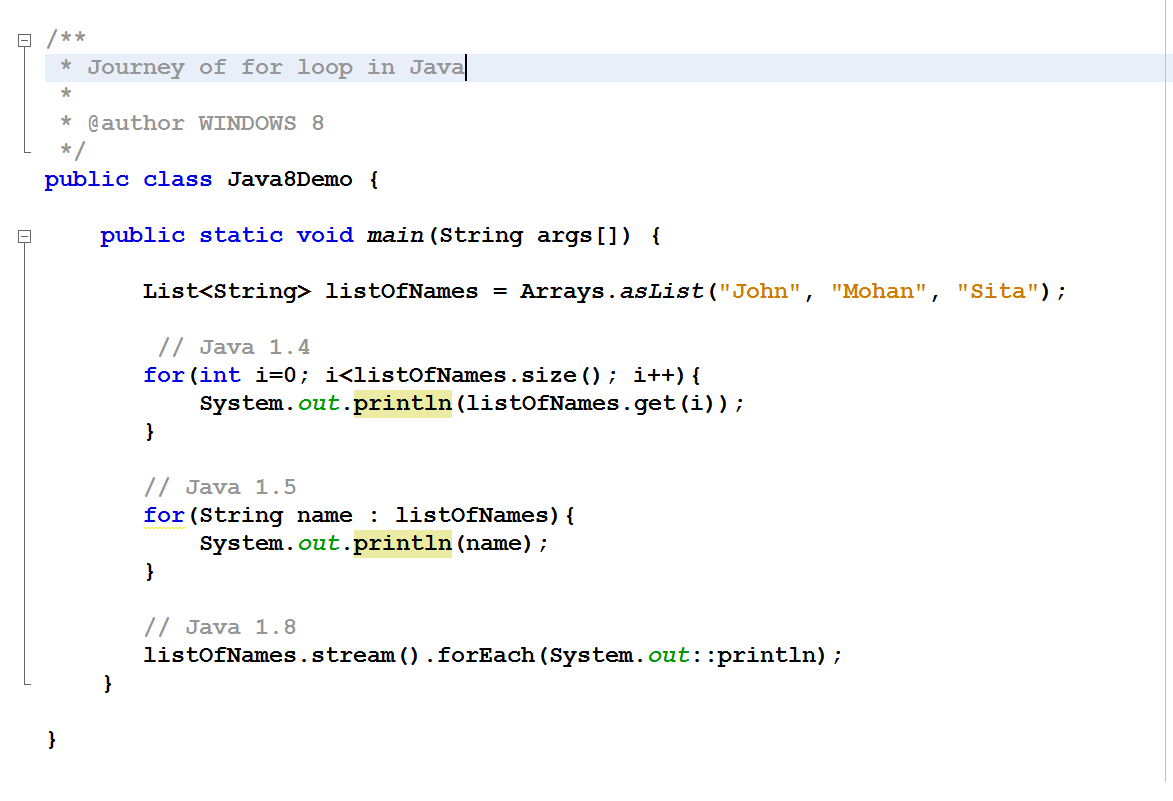
Java 8 Journey of for loop in Java, for(index) to forEach()
In this Java concurrency tutorial, you will understand how ReadWriteLock works and use it for simple cases with ReentrantReadWriteLock implementation.. Basically, a ReadWriteLock is designed as a high-level locking mechanism that allows you to add thread-safety feature to a data structure while increasing throughput by allowing multiple threads to read the data concurrently and one thread to.

Java并发编程第二讲各种各样的锁_unlock trylock_WJ的博客CSDN博客
The tryLock () method of ReentrantLock class holds the lock only when any other thread does not hold it at the time of invocation. If the current thread already holds this lock, then the hold count is incremented by one, and the method returns true. Otherwise false. Syntax public boolean tryLock ()

Java线程池ThreadPoolExecutor使用和分析(三) 终止线程池原理 Trust_FreeDom 博客园
Java Lock.tryLock Examples Programming Language: Java Namespace/Package Name: java.util.concurrent.locks Class/Type: Lock Method/Function: tryLock Examples at hotexamples.com: 30 java.util.concurrent.locks is the package library in Java that provides high-performance synchronization and locking mechanisms.

Java do while loop DigitalOcean
Welcome to Java Lock example tutorial. Usually when working with multi-threaded environment, we use synchronized for thread safety. Java Lock Most of the times, synchronized keyword is the way to go but it has some shortcomings that lead the way to inclusion of Lock API in Java Concurrency package.

Java多线程问题方法lock.lockInterruptibly()、tryLock()和tryLock(long timeout,TimeUint uint)的用法和区别CSDN博客
Lock in Java with java tutorial, features, history, variables, object, programs, operators, oops concept, array, string, map, math, methods, examples etc.. The tryLock() method is mainly used at the time of invocation for acquiring the lock. It returns the lock immediately with the Boolean value true when the lock is available.
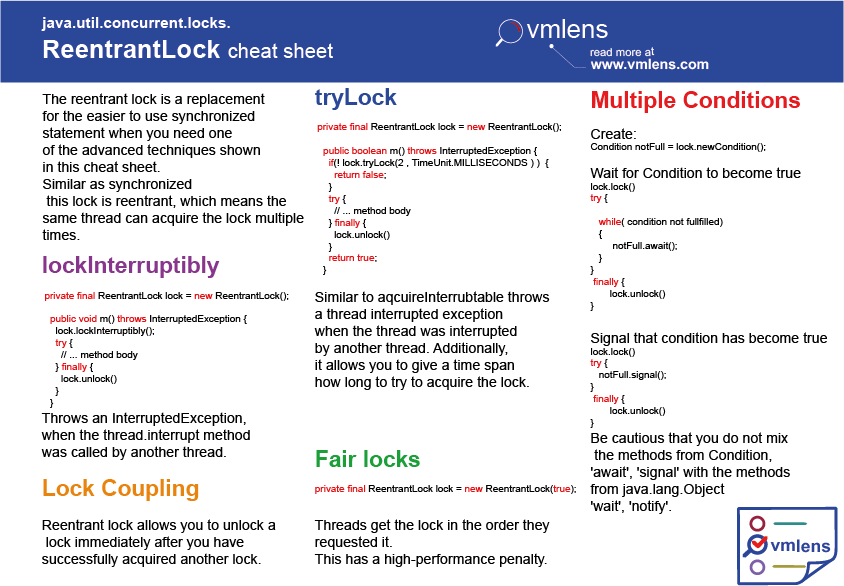
ReentrantLock Cheat Sheet DZone Java
A java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock is a thread synchronization mechanism just like synchronized blocks. A Lock is, however, more flexible and more sophisticated than a synchronized block. Since Lock is an interface, you need to use one of its implementations to use a Lock in your applications.
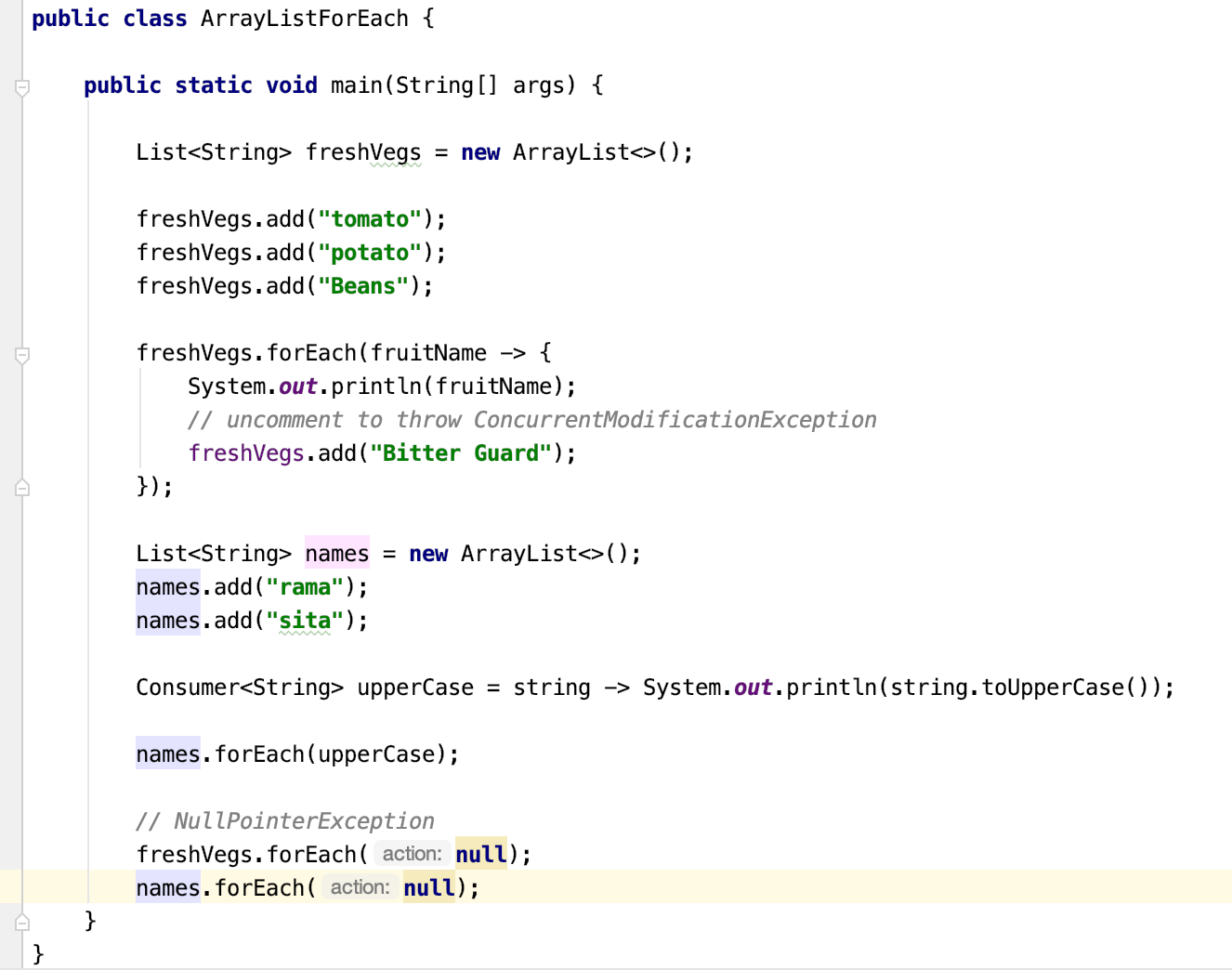
Java 8 ArrayList forEach Examples
The Lock API provides tryLock () method. The thread acquires lock only if it's available and not held by any other thread. This reduces blocking time of thread waiting for the lock. A thread that is in "waiting" state to acquire the access to synchronized block can't be interrupted.

Multithreading in Java 42 tryLock() Method of ReentrantLock Class in java YouTube
Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns immediately with the value true, setting the lock hold count to one. Even when this lock has been set to use a fair ordering policy, a call to tryLock() will immediately acquire the lock if it is available, whether or not other threads are currently waiting for the lock. This.

Practical example for pthread_mutex_trylock YouTube
All Implemented Interfaces: Serializable, Lock public class ReentrantLock extends Object implements Lock, Serializable A reentrant mutual exclusion Lock with the same basic behavior and semantics as the implicit monitor lock accessed using synchronized methods and statements, but with extended capabilities.

Thread in Java Java threads Create a thread in Java Thread lifecycle
public class LocKTest { @Test public void testLock () { Lock lock = new ReentrantLock (); while (true) { if (lock.tryLock ()) { //lock.lock (); same result if I include an explicit lock here System.out.println ("has been locked"); } } } } As far as I understood, tryLock will lock the ReentrantLock if possible (ie if not locked yet).
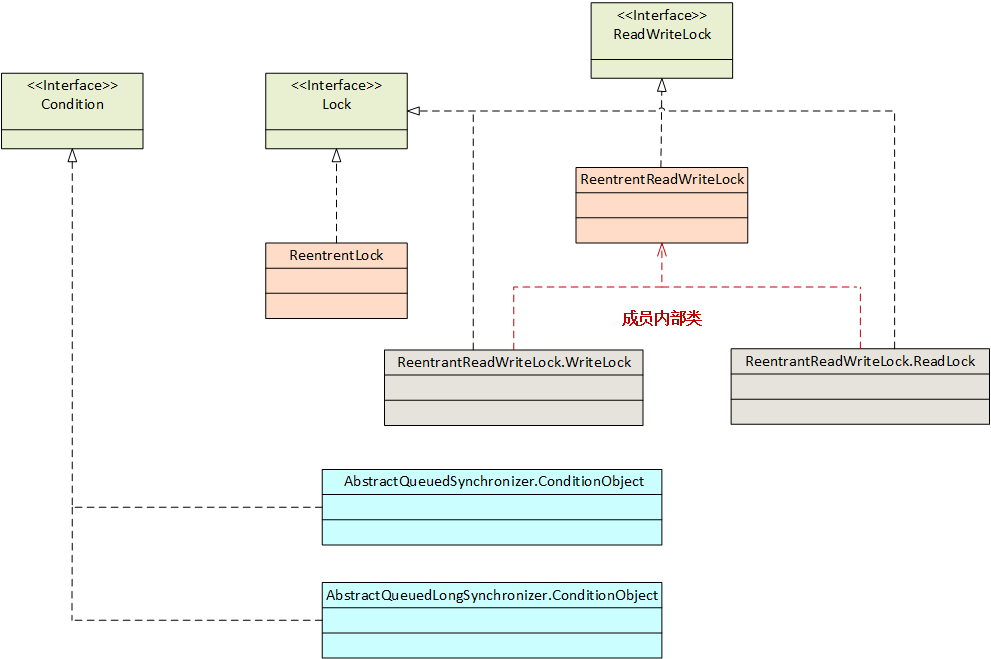
Java 并发开发:Lock 框架详解
Let's get started. 1st let's understand each of these terms and then we will go over working example. Lock (): java.util.concurrent.locks. A lock is a thread synchronization mechanism like synchronized blocks except locks can be more sophisticated than Java's synchronized blocks.

Java ReentrantLock fairness, tryLock and more YouTube
Introduction to File Locks In general, there are two types of locks: Exclusive locks — also known as write locks Shared locks — also referred to as read locks Put simply, an exclusive lock prevents all other operations - including reads - while a write operation completes.

Java tutorial tewstracks
4 Answers Sorted by: 4 One straight-forward use case is a thread processing a batch of elements, occasionally trying to commit the elements that have been processed. If acquiring the lock fails, the elements will be committed in the next successful attempt or at the final, mandatory commit.

Java Lock Example ReentrantLock [Latest] All Learning
Create Reentrant Lock Locking and Unlocking a Java Lock Fail-safe Lock and Unlock Example Lock Protected Counter Lock Reentrance Lock Fairness Lock and ReentrantLock Methods lock () lockInterruptibly () tryLock () trylock (long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) unlock () getHoldCount () getQueueLength () hasQueuedThread () hasQueuedThreads () isFair ()

Java并发编程第二讲各种各样的锁_trylock unlock_WJ的博客CSDN博客
Java public void some_method () { reentrantlock.lock (); try { } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace (); } finally { reentrantlock.unlock (); } } Unlock statement is always called in the finally block to ensure that the lock is released even if an exception is thrown in the method body (try block).

java语言中锁方法 lock 与 trylock 使用 简书
Return. The method tryLock() returns true if the lock was acquired and false otherwise . Example The following code shows how to use Lock from java.util.concurrent.locks.. Specifically, the code shows you how to use Java Lock tryLock() . Example 1